Clinical Pharmacogenetics in Pediatric Patients
Newborns and infants rapidly undergo simultaneous stages of organ growth and demonstrate large variability in drug response and metabolizing capabilities.[1,2] The enzymes, transporters and targets important for pediatric drugs all have the potential to vary along developmental timelines in terms of affinity, functional capacity and expression. Drug-metabolizing enzymes can vary according to chronological age.[3,4]
As such, determining gene expression patterns at various ontological periods becomes of key importance in formulating treatment plans for pediatric patients. Exposure to toxins or pharmaceutical agents or lack of medical treatment of a particular illness at sensitive periods of development could irreversibly disrupt the normal maturation of an individual. Observable consequences of such disruption may not appear until much later in life. READ MORE….
ASTHMA excerpt: Polymorphisms (lack of specific enzyme in individuals) have been identified within the molecular proteins and enzymes involved in the pathways by which such drugs (vaccine excipients) may bring about their effects that may influence inter-individual variation in patient response.
What is Cytochrome P450 and what does it have to do with drugs and vaccine metabolism and adverse reactions?
Cytochrome P-450 is the liver’s enzyme system and is responsible for most drug metabolism. Numerous medications, nutrients, and herbal therapies are metabolized through the cytochrome P450 (CYP450) enzyme system. This system can be inhibited or induced by drugs including excipients in vaccines. It is to be noted that cytochrome P450 is maturing and is immature in infants who are regularly vaccinated with Hepatitis B as early as one hour and those who receive the Vitamin K injection.
There are more than 50 CYP450 enzymes, but the CYP1A2, CYP2C19, CYP2D6, CYP1A2, CYP3A4, and CYP3A5 enzymes are responsible for metabolizing 45% of drug metabolism. The CYP2D6 (20–30%), the CYP2C9 (10%) and the CYP2E1 and CYP1A2 (5%) complete this enzyme system. Many ingredients in vaccines inhibit Cytochrome P450, therefore the offending agent remains in the body of the infant and toddler and act as a poison damaging the mitachondria found in every cell in the body except for the blood. If a medication is taken with an agent that inhibits its metabolism, then the toxin level can rise and result in a harmful or adverse effect.
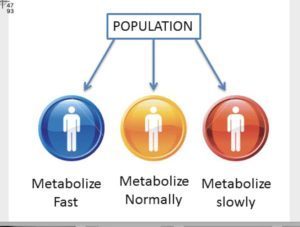
But it is not only that “all” infants have immature Cyp 450 enzymes. For example, 10% of Caucasians are non-metabolizers (Cyp 450 2D6). For their whole life long these poor (polymorphic) metabolizers cannot metabolize 20-30% of drugs. 7% of African Americans are poor/non metabolizers of drugs dependent on CYP2D6. Due to hereditary genetic variations (not defects) they do not have the activity of Cyp 2D6. That means that children and teens given drugs such as Adderall, Haldol, Respiridal; street drugs like LSD, psilosybn, cocaine, codeine without adequate genetic pre-testing are likely to have “drug induced psychosis”; suicidal ideation, homicidal ideations by which “heinous” thoughts drive them to such violence as school shootings and mass attacks.
Cyp 450 superfamilies in infants and children.
Synopsis: Infants do not have a mature liver or liver enzyme function such as Cytochrome P450 and its various metabolites until the age of three years old. Hence upwards of 36 vaccine doses by 18 months old containing the above excipients are poisoning the world’s emerging humanity.:
Study #2: Immaturity of Cyp 450 in Neonate boys (book)
Study #3 (2018) The Ontogeny of Cytochrome P450 Enzyme Activity and Protein Abundance in Conventional Pigs in Support of Preclinical Pediatric Drug Research
Comprehensive Vaccine Ingredient Information- CDC VACCINE EXCIPIENTS LIST PER VACCINE CDC Vaccine excipients-table-2
DIRECT LIST OF THE XENOBIOTIC INGREDIENTS IN VACCINES
Medical treatments and drug protocols including vaccines should be implemented within a framework of the patient’s heritage, race, and culture in order to provide effective management modalities. Infants as well as adults should be assessed for their ability to metabolize the ingredients in vaccines.
When in comes to diet, CYP450 inducers and inhibitors are commonly ingested items such as grapefruit juice (inhibitor) and tobacco and herbs such as St. John’s Wort (inducers). In the case of grapefruit juice, there are numerous medications known to interact with grapefruit juice including statins, antiarrhythmic agents, immunosuppressive agents, and calcium channel blockers. Furthermore, the inhibition of the enzyme system seems to be dose dependent; thus, the more a patient drinks, the more the inhibition that occurs. Additionally, the effects can last for several days if grapefruit juice is consumed on a regular basis. Luckily, the effect of this is not seen with other citrus juices.
Hopefully, this brief review has opened the door to your inquisitive nature on how the liver’s enzyme system is effected by numerous medications and vaccine excipients and why some patients experience clinically significant unanticipated adverse reactions or therapeutic failures.
The above was edited and altered to include vaccines excipients from Davis’ Drug Guide
Effects of Polysorbate 80, a widely used ingredient in vaccines
The results indicate that these non-ionic surfactants are in vitro inhibitors of CYP-mediated metabolism and might have the potential to modify the pharmacokinetics of co-administered drugs, which are substrates of CYP, and thereby enhance their bioavailability.
More on Polysorbate 80 and Polysorbate 20
The vaccine ingredients effects on the human body, followed by links to substantiating documentation of causation
Comprehensive Vaccine Ingredient Information- CDC VACCINE EXCIPIENTS LIST PER VACCINE CDC Vaccine excipients-table-2
Vaccination ingredients according to the product insert:
MMR II: Measles, Mumps and Rubella
http://www.merck.com/product/usa/pi_circulars/m/mmr_ii/mmr_ii_pi.pdf
The Ingredients: measles, mumps, rubella virus, neomycin, sorbitol, hydrolized gelatin, chick embryonic fluid, and human diploid cells from aborted fetal tissue.
Infanrix: Dipthetheria, Tetanus and Pertussis
http://us.gsk.com/products/assets/us_infanrix.pdf
The Ingredients: Diphtheria, Tetanus and Pertussis toxoids, 2-Phenoxyethanol, Aluminum hydroxide, and Formaldehyde.
IPOL: Polio
http://www.vaccineshoppe.com/US_PDF/IPOL_942420_11.06.pdf
The Ingredients: 3 types of polio viruses, neomycin, streptomycin, polymyxin B, formaldehyde, 2-phenoxyethenol, and a continuous line of monkey kidney cells.
Act-Hib: Haeomophilus Influenza type B
http://www.novaccine.com/pdffiles/Act_HIB_package_insert.pdf
The Ingredients: Haemophilus influenza Type B, polyribosylribitol phosphate, ammonium sulfate, formalin, and sucrose.
Menactra: Meningococcal
www.fda.gov/CbER/products/menactra.htm
The Ingredients: Neisseria meningitidis A, C, Y and W-135 strains, Mueller Hinton Agar, Watson Scherp Media, polysaccharide antigens, formaldehyde, diphtheria toxoid protein, ammonium sulfate.
Prevnar: Pneumococcal
http://www.wyeth.com/content/showlabeling.asp?id=134
The Ingredients: saccharides from capsular Streptococcus pneumoniae antigens (7 serotypes) individually conjugated to diphtheria CRM 197 protein, aluminum phosphate, ammonium sulfate, soy protein, and yeast.
Varivax: Varicella (chickenpox)
www.merck.com/product/usa/pi_circulars/v/varivax/varivaxpi.pdf
The Ingredients: varicella live virus, neomycin, phosphate, sucrose, and monosodium glutamate (MSG), processed gelatin, fetal bovine serum, guinea pig embryo cells, albumin from human blood, and human diploid cells from aborted fetal tissue.
Rotarix: Rotavirus
http://www.fda.gov/CbER/label/rotarixLB.pdf
The Ingredients: weakened human rotavirus, dextran, sorbitol, xanthan, Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium (DMEM), which contains: sodium chloride, potassium chloride, magnesium sulphate, ferric (III) nitrate, sodium phosphate, sodium pyruvate, D-glucose, concentrated vitamin solution, L-cystine, L-tyrosine, amino acids solution, L-glutamine, calcium chloride, sodium hydrogenocarbonate, and phenol red.
Gardasil:HPV
http://www.merck.com/product/usa/pi_circulars/g/gardasil/gardasil_pi.pdf
The Ingredients: HPV types 6, 11, 16 and 18, saccharomyces cerevisiae, “fermentation media”, aluminum, sodium chloride, polysorbate 80, sodium borate.
FluZone (or FluShield, same product): Influenza
www.fda.gov/CBER/label/fluzoneLB.pdf
The Ingredients: Trivalent influenza virus, gentamicin sulphate, formaldehyde, thimerosal, polysorbate 80 (Tween 80) and chick embryonic fluid
Havrix: Hepatitis A
http://us.gsk.com/products/assets/us_havrix.pdf
Ingredients: Hepatitis A virus/toxoids, formalin, aluminum hydroxide, 2-phenoxyethanol, polysorbate 20, and residual MRC5 proteins -human diploid cells from aborted fetal tissue.
Energix B: Hepatitis B
http://us.gsk.com/products/assets/us_engerixb.pdf
The Ingredients: genetic sequence of the hepatitis B virus that codes for the surface antigen (HbSAg), cloned into GMO yeast, aluminum hydroxide, and thimerosal.
———————————————————————–
What’s in the vaccine that needs Cyp450 to metabolize?
Comprehensive list of Xenobiotics in Vaccines: MUST SEE LIST
Aluminum= Neurotoxin
http://informedcitizensagainstvaccination.blogspot.com/2009/11/aluminum-neurotoxic-vaccine-adjuvant.html
Formaldehyde= Carcinogen (cancer causer); linked causally to an assortment of cancers, most recently Leukemia. The International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) classified it as a known human carcinogen in 2004.
http://informedcitizensagainstvaccination.blogspot.com/2009/11/formaldehyde-carcinogen-in-vaccinations.html
Thimerosal (mercury)= Neurotoxin; controversially linked to Autism in the media, but is well known and causally proven to cause many neurological disorders, cell death in the brain, mitochondrial damage, etcetera. Thimerosal is still being used in the Hepatitis B and Influenza vaccines as of 2009, and is also contained within several of the H1N1 vaccinations.
http://informedcitizensagainstvaccination.blogspot.com/2009/11/thimerosal-neurotoxic-in-plethora-of.html
2-Phenoxyethanol aka “Antifreeze” aka “ethylene glycol monomethyl ether”= neurotoxic, CNS toxicant.
http://informedcitizensagainstvaccination.blogspot.com/2009/11/2-phenoxyethanol-antifreeze-neurotoxin.html
Phenol= nephrotoxic; CNS toxin, heart toxin, gastrointestinal, kidney, lung and blood vessel toxin… known to induce coma’s and death; by far one of the most toxic of all vaccine ingredients.
http://informedcitizensagainstvaccination.blogspot.com/2009/11/phenol-cns-toxin-causes-comas-and-death.html
Sorbitol= cardiac toxin, causes neuropathy in and exacerbation of diabetes, CNS toxin, our own government states under no uncertain terms that this substance is NOT to be injected… then allows it to be used in childhood vaccinations.
http://informedcitizensagainstvaccination.blogspot.com/2009/11/sorbitol-cardiac-toxin-causes.html
Neomycin, Streptomycin, Polyxmyxin B, Gentamicin Sulfate= Antibiotics. Immune suppressing, lead to the development of more virulent organisms and antibacterial resistance so people cannot combat them.
http://informedcitizensagainstvaccination.blogspot.com/2009/11/antibiotics-in-vaccinations.html
Egg (chick embryonic fluid), soy, yeast, gelatin= Allergens, risk of anaphylaxis and the development of Asthma.
http://informedcitizensagainstvaccination.blogspot.com/2009/11/allergens-in-vaccinations.html
Monosodium Glutamate= Excitotoxin; hazardous to your health in so many ways: read the full length article for further details.
http://informedcitizensagainstvaccination.blogspot.com/2009/11/monosodium-glutmate-creating-dumb-obese.html
Polysorbate 80 or Tween 80= anaphylaxis risk, also permeates the BBB (blood brain barrier) which means vaccine toxins can enter the brain.
http://informedcitizensagainstvaccination.blogspot.com/2009/11/polysorbate-80-aka-tween-80-allows.html
Chick embryonic fluid, fetal bovine serum, guinea pig embryo cells, monkey kidney cells= Animal products in vaccinations that are highly susceptible to contamination. There is a particularly elevated risk with bovine serum (bovine polyomavirus) and monkey kidney cells (SV40 contamination causing cancer).
What is in the “mediums“? https://vaccineliberationarmy.com/2019/01/15/dogs-cats-increasingly-receiving-psyche-drugs-as-in-humans-its-the-vaccines/
Animal Products (Contaminants) in Vaccinations
Animal products in vaccination: Monkey kidney cells, sheep red blood cells, chick embryonic fluid, fetal bovine serum, bovine gelatin, guinea pig embryo cells= risk and history of contamination.
Calf fetus, chick embryo, chick kidney, chicken egg, cow heart, dog kidney, duck egg, guinea pig embryo, horse blood, monkey kidney, monkey lung, mouse blood, pig blood, rabbit brain, sheep blood and others. These are used in various vaccine production lines. Residues are not completely purified out of the final packaged product. Contamination can introduce new pathogens. READ MORE…
List of ingredients and levels of carcinogenicity, for each, etc.
See also:
The dangerous impurities of vaccines by Janine Roberts
On the toxic ingredients of vaccinations: plays special emphasis to animal by-products and their production process in vaccinations.
http://www.foresight-preconception.org.uk/pdf/dangerous-impurities-of-vaccines.pdf
 Joske Millecam
Joske Millecam Laura De Clerck
Laura De Clerck Elisabeth Govaert2,
Elisabeth Govaert2,  Elke Gasthuys
Elke Gasthuys Dieter Deforce
Dieter Deforce Siska Croubels
Siska Croubels